43 indexing using labels in dataframe
Pandas Boolean Indexing: How to Use Boolean Indexing Pandas Boolean Indexing. Pandas boolean indexing is a standard procedure. We will select the subsets of data based on the actual values in the DataFrame and not on their row/column labels or integer locations. Pandas indexing operators "&" and "|" provide easy access to select values from Pandas data structures across various use cases. Boolean Indexing in Pandas - GeeksforGeeks In boolean indexing, we will select subsets of data based on the actual values of the data in the DataFrame and not on their row/column labels or integer locations. In boolean indexing, we use a boolean vector to filter the data. Boolean indexing is a type of indexing that uses actual values of the data in the DataFrame.
pandas select from Dataframe using startswith - Stack Overflow Then I realized I needed to select the field using "starts with" Since I was missing a bunch. So per the Pandas doc as near as I could follow I tried criteria = table['SUBDIVISION'].map(lambda x: x.startswith('INVERNESS')) table2 = table[criteria]

Indexing using labels in dataframe
Pandas DataFrame index and columns attributes - JournalDev Pandas DataFrame index and columns attributes allow us to get the rows and columns label values. We can pass the integer-based value, slices, or boolean. search. ... We can't set the columns label value using this attribute. Let's look at some examples of using the DataFrame columns attribute. We will reuse the earlier defined DataFrame ... Indexing a Pandas DataFrame for people who don't like to remember things In pandas data frames, each row also has a name. By default, this label is just the row number. However, you can set one of your columns to be the index of your DataFrame, which means that its values will be used as row labels. We set the column 'name' as our index. It is a common operation to pick out one of the DataFrame's columns to work on. Label-based indexing to the Pandas DataFrame - GeeksforGeeks In the above example, we use the concept of label based Fancy Indexing to access multiple elements of data frame at once and hence create two new columns ' Age ' and ' Marks ' using function dataframe.lookup () Example 3: Python3 import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame ( [ ['Date1', 1850, 1992,'Avi', 5, 41, 70, 'Avi'],
Indexing using labels in dataframe. pandas.DataFrame.set_index — pandas 1.4.2 documentation DataFrame.set_index(keys, drop=True, append=False, inplace=False, verify_integrity=False) [source] ¶ Set the DataFrame index using existing columns. Set the DataFrame index (row labels) using one or more existing columns or arrays (of the correct length). The index can replace the existing index or expand on it. Parameters Pandas Set Column as Index in DataFrame - Spark by {Examples} Use DataFrame.set_index() method to set the existing column of DataFrame as an index. On DataFrame, the row label is an Index. If your DataFrame has already had an Index, this replaces the existing index or expands on it. You can set the DataFrame index (row labels) using one or more existing columns or arrays (of the correct length). Syntax: Pandas: Create an index labels by using 64-bit integers, floating-point ... Using an additional state variable, such as an index variable (which you would normally use in languages such as C or PHP), is considered non-pythonic. The better option is to use the built-in function enumerate (), available in both Python 2 and 3: for idx, val in enumerate (ints): print (idx, val) Example: ints = [8, 23, 45, 12, 78] Indexing and selecting data — pandas 1.4.2 documentation pandas provides a suite of methods in order to have purely label based indexing. This is a strict inclusion based protocol. Every label asked for must be in the index, or a KeyError will be raised. When slicing, both the start bound AND the stop bound are included, if present in the index.
Pandas DataFrame Indexing - KDnuggets In pandas data frames, each row also has a name. By default, this label is just the row number. However, you can set one of your columns to be the index of your DataFrame, which means that its values will be used as row labels. We set the column 'name' as our index. It is a common operation to pick out one of the DataFrame's columns to work on. pandas Tutorial => Slicing with labels Filtering / selecting rows using `.query ()` method. Filtering columns (selecting "interesting", dropping unneeded, using RegEx, etc.) Get the first/last n rows of a dataframe. Mixed position and label based selection. Path Dependent Slicing. Select by position. Select column by label. Select distinct rows across dataframe. Slicing with labels. How to Select Columns by Index in a Pandas DataFrame If you'd like to select columns based on label indexing, you can use the .loc function. This tutorial provides an example of how to use each of these functions in practice. Example 1: Select Columns Based on Integer Indexing. The following code shows how to create a pandas DataFrame and use .iloc to select the column with an index integer ... Python Pandas - Indexing and Selecting Data - Tutorials Point Pandas provide various methods to have purely label based indexing. When slicing, the start bound is also included. Integers are valid labels, but they refer to the label and not the position. .loc () has multiple access methods like − A single scalar label A list of labels A slice object A Boolean array
Working With Specific Values In Pandas DataFrame - Data Courses This function of a pandas DataFrame is of high value as you can build an index using a specific column, (meaning: a label) that you want to use for managing and querying your data. For example, one can develop an index from a column of values and then use the attribute.loc to select data from pandas DataFrame based on a value found in the index. Pandas Select Rows by Index (Position/Label) In this article, I will explain how to select rows from pandas DataFrame by integer index and label, by the range, and selecting first and last n rows with several examples. loc [] & iloc [] operators are also used to select columns from pandas DataFrame and refer to related article how to get cell value from pandas DataFrame. Set Index in pandas DataFrame - PYnative This function is used to re-assign a row label using the existing column of the DataFrame. It can assign one or multiple columns as a row index. Let's see how to use DataFrame.set_index() function to set row index or replace existing. Syntax. DataFrame.set_index(keys, drop=True, append=False, inplace=False, verify_integrity=False) Parameters Indexing, Slicing and Subsetting DataFrames in Python Indexing by labels loc differs from indexing by integers iloc. With loc, both the start bound and the stop bound are inclusive. When using loc, integers can be used, but the integers refer to the index label and not the position. For example, using loc and select 1:4 will get a different result than using iloc to select rows 1:4.
Delete column/row from a Pandas dataframe using .drop() method Feb 02, 2020 · Columns can be removed permanently using column name using this method df.drop(['your_column_name'], axis=1, inplace=True). To drop a single column from pandas dataframe, we need to provide the name of the column to be removed as a list as an argument to drop function. Remember parameter self? Pandas .drop() function can drop column or row.
Pandas DataFrame Indexing: Set the Index of a Pandas Dataframe Python list as the index of the DataFrame In this method, we can set the index of the Pandas DataFrame object using the pd.Index (), range (), and set_index () function. First, we will create a Python sequence of numbers using the range () function then pass it to the pd.Index () function which returns the DataFrame index object.
How to select subset of data with Index Labels? - Tutorials Point The .loc attribute selects only by index label, which is similar to how Python dictionaries work. Select a Subset Of Data Using Index Labels with .loc [] The loc and iloc attributes are available on both Series and DataFrame Import the movies dataset with the title as index.
Indexing in Pandas Dataframe using Python - Medium Indexing using .loc method. If we use the .loc method, we have to pass the data using its Label name. Single Row To display a single row from the dataframe, we will mention the row's index name in the .loc method. The whole row information will display like this, Single Row information Multiple Rows
Tutorial: How to Index DataFrames in Pandas - Dataquest Let's explore four methods of label-based dataframe indexing: using the indexing operator [], attribute operator ., loc indexer, and at indexer. Using the Indexing Operator If we need to select all data from one or multiple columns of a pandas dataframe, we can simply use the indexing operator [].
Indexing and Sorting a dataframe using iloc and loc Labels based indexing using loc. To index a dataframe based on column names, loc can be used. For example, to get all the columns between petal_length till iris class and records from 2nd to 10th, can be extracted by using - ... Simples way to sort a dataframe can be done using sort_values function of pandas dataframe, which take the column ...
How to get the names (titles or labels) of a pandas data frame in python To get the names of the data frame rows: >>> df.index Index(['Alice', 'Bob', 'Emma'], dtype='object') Get the row names of a pandas data frame (Exemple 2) Another example using the csv file train.csv (that can be downloaded on kaggle): >>> import pandas as pd >>> df = pd.read_csv('train.csv') >>> df.index RangeIndex(start=0, stop=1460, step=1)
How to Select Rows by Index in a Pandas DataFrame - Statology .iloc selects rows based on an integer index. So, if you want to select the 5th row in a DataFrame, you would use df.iloc [ [4]] since the first row is at index 0, the second row is at index 1, and so on. .loc selects rows based on a labeled index. So, if you want to select the row with an index label of 5, you would directly use df.loc [ [5]].
Python | Pandas DataFrame - GeeksforGeeks Jan 10, 2019 · Indexing a DataFrame using .loc[ ]: This function selects data by the label of the rows and columns. The df.loc indexer selects data in a different way than just the indexing operator. It can select subsets of rows or columns. It can also simultaneously select subsets of rows and columns. Selecting a single row
How to Get the Index of a Dataframe in Python Pandas? Method 1: Using for loop. In Python, we can easily get the index or rows of a pandas DataFrame object using a for loop. In this method, we will create a pandas DataFrame object from a Python dictionary using the pd.DataFrame () function of pandas module in Python. Then we will run a for loop over the pandas DataFrame index object to print the ...
How to Index Data in Pandas with Python - Medium Here we can see that the index or label of 3 is True (in the 4th row), which means that the first row we will see once we use this array of boolean values with our loc method is the row with the label 3 (or 4th row in our ufo dataframe). ufo.loc [ufo.City == 'Abilene', :] ufo sightings in Abilene And that is exactly what we see!
How to find index of value in Pandas dataframe - DevEnum.com 2. df.index.values to Find index of specific Value. To find the indexes of the specific value that match the given condition in Pandas dataframe we will use df ['Subject'] to match the given values and index. values to find an index of matched value. The result shows us that rows 0,1,2 have the value 'Math' in the Subject column.
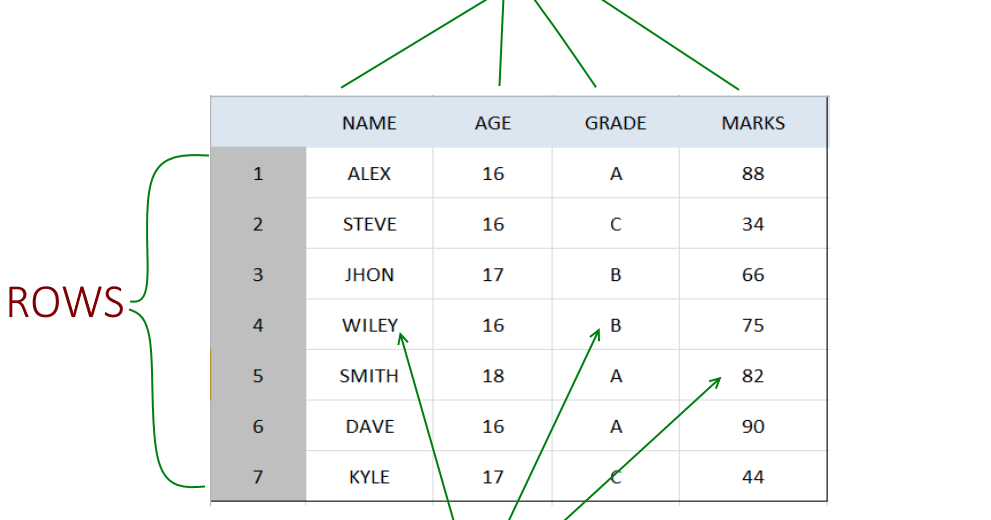
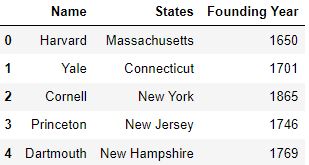
The Pandas DataFrame: Make Working With Data Delightful This Pandas DataFrame looks just like the candidate table above and has the following features: Row labels from 101 to 107; Column labels such as 'name', 'city', 'age', and 'py-score' Data such as candidate names, cities, ages, and Python test scores; This figure shows the labels and data from df:
Python Pandas: Get Index Label for a Value in a DataFrame If I know the value in 'hair' is 'blonde', how do I get the index label (not integer location) corresponding to df.ix['mary','hair']? (In other words, I want to get 'mary' knowing that hair is 'blonde'). If I wanted the integer value of the index I'd use get_loc. But I want the label. Thanks in advance.
MultiIndex / advanced indexing — pandas 1.4.2 documentation A MultiIndex can be created from a list of arrays (using MultiIndex.from_arrays()), an array of tuples (using MultiIndex.from_tuples()), a crossed set of iterables (using MultiIndex.from_product()), or a DataFrame (using MultiIndex.from_frame()). The Index constructor will attempt to return a MultiIndex when it is passed a list of tuples. The ...
Label-based indexing to the Pandas DataFrame - GeeksforGeeks In the above example, we use the concept of label based Fancy Indexing to access multiple elements of data frame at once and hence create two new columns ' Age ' and ' Marks ' using function dataframe.lookup () Example 3: Python3 import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame ( [ ['Date1', 1850, 1992,'Avi', 5, 41, 70, 'Avi'],
Indexing a Pandas DataFrame for people who don't like to remember things In pandas data frames, each row also has a name. By default, this label is just the row number. However, you can set one of your columns to be the index of your DataFrame, which means that its values will be used as row labels. We set the column 'name' as our index. It is a common operation to pick out one of the DataFrame's columns to work on.






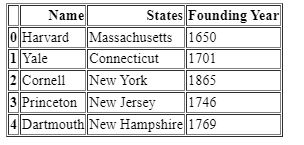



Post a Comment for "43 indexing using labels in dataframe"